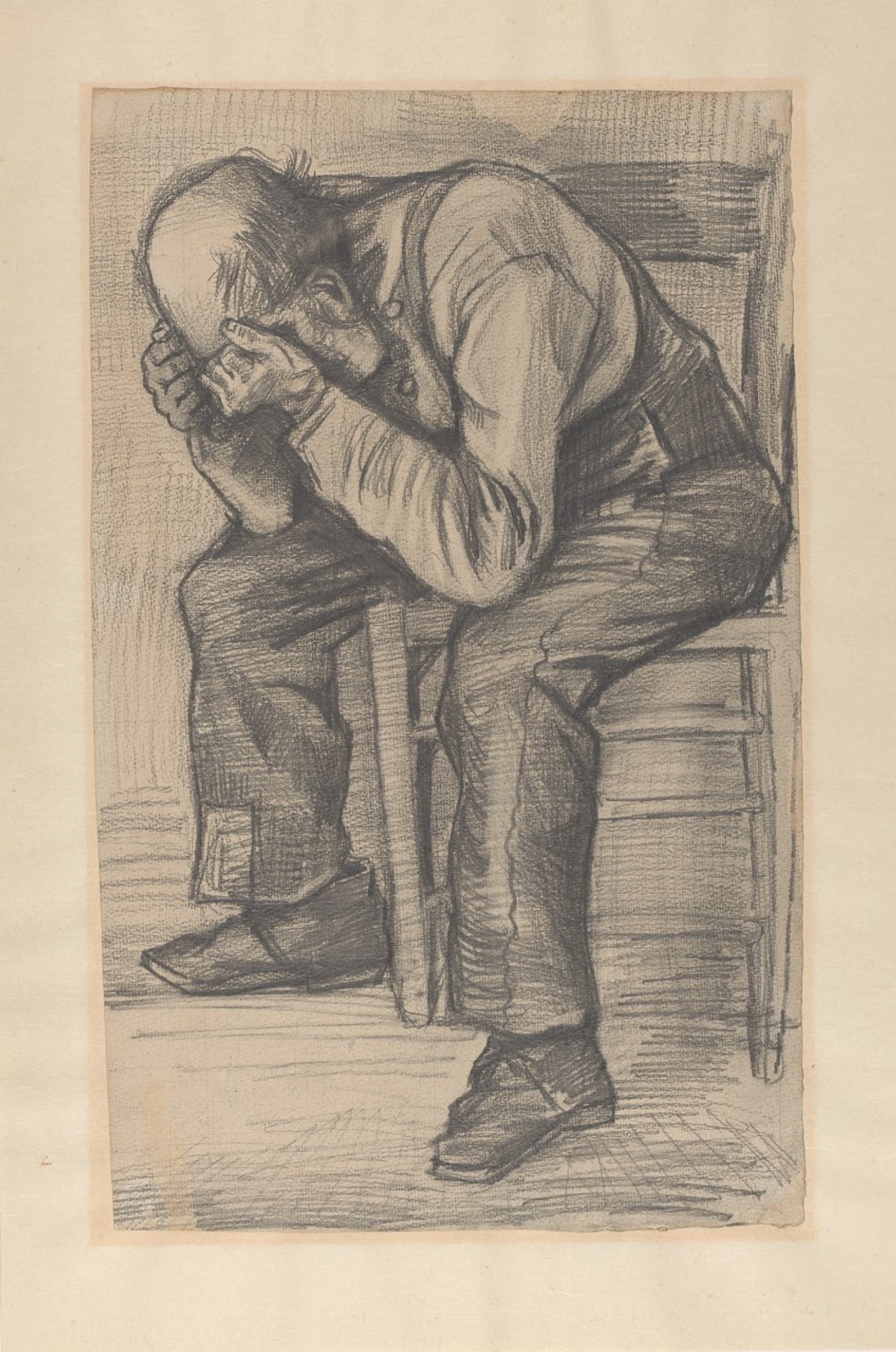
The Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam has authenticated a preliminary sketch for Worn out, a drawing made in November 1882 while the artist was working in The Hague. Teio Meedendorp, the museum’s senior researcher, describes it as “a stunning contribution” to the oeuvre.
The sketch represents a key subject, since in 1890 Van Gogh turned the composition into one of his most powerful paintings, Sorrowing Old Man. The elderly man sits with his head in his hands, either from exhaustion or misery.
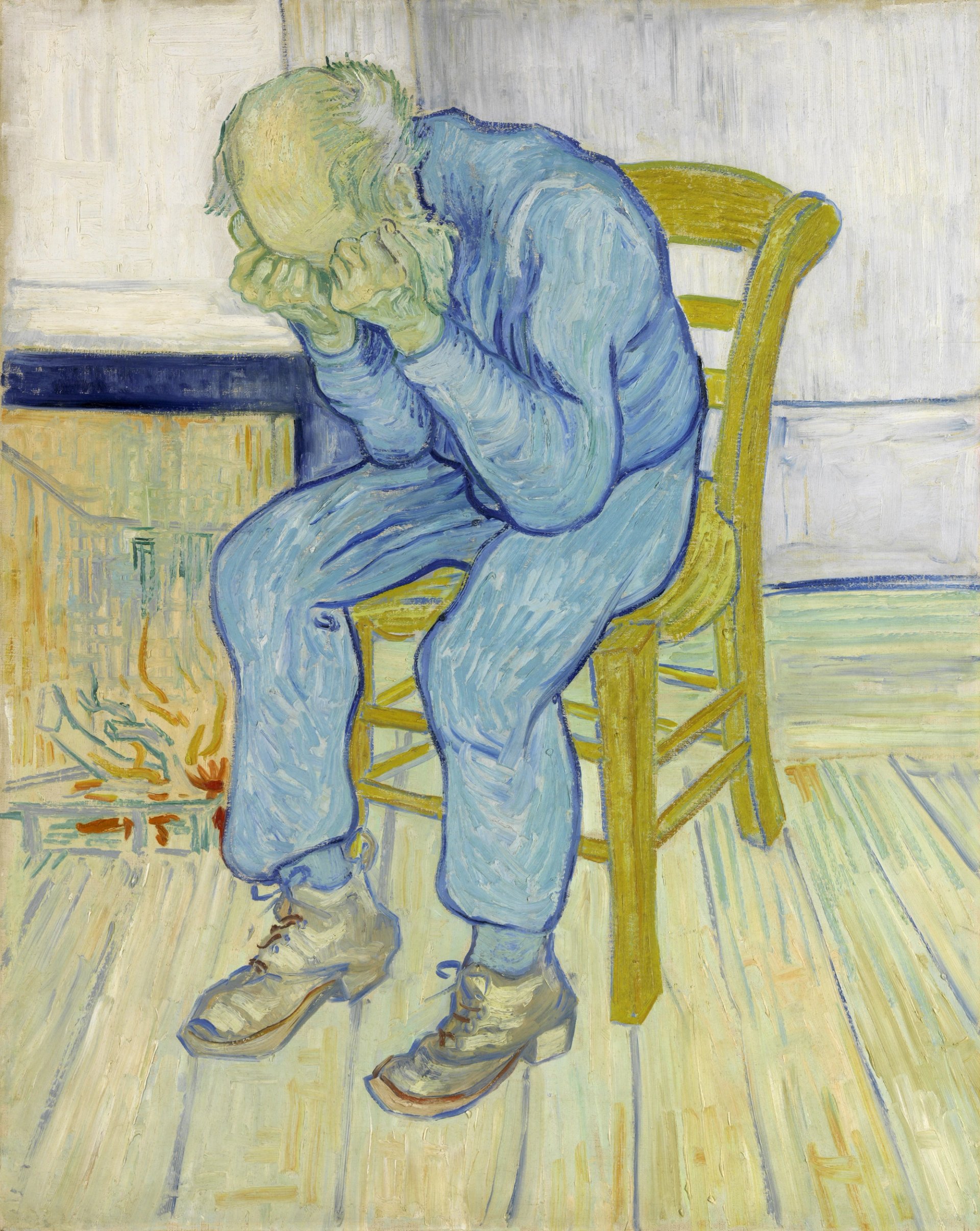

Van Gogh’s Sorrowing Old Man, also known as At Eternity’s Gate (May 1890) Courtesy of the Kröller-Müller Museum, Otterlo
Meedendorp’s detailed study on the newly discovered sketch will be published in the October issue of The Burlington Magazine. In the meantime it is freely available online.
The newly discovered sketch, in an unnamed Dutch private collection, was acquired in 1900-10 and then passed down the family. Nothing is known of its whereabouts in the 1880s and 90s. Earlier this year the family approached the Van Gogh Museum, requesting that it be authenticated.
Meedendorp confirmed the authenticity: “In stylistic terms, it fits perfectly with the many figure studies we know from Van Gogh’s time in The Hague and the connection with final version of Worn out is obvious.”
According to Meedendorp, in terms of materials “you find everything you’d expect in a Van Gogh drawing from this period: a thick carpenter’s pencil as medium, coarse watercolour paper as support, and fixing the image with a solution of water and milk”. The paper has a Hallines watermark of a type that the artist often used in The Hague. On the reverse of the sheet is a very rough sketch of a farmer in a field.
The sketch of Worn out offers an unusual insight into Van Gogh’s method of working. He began by drawing a grid on the paper (only just visible in reproductions) and then used a perspective frame to view the seated man and capture his figure quickly in the correct proportions. Van Gogh worked up the sketch in his characteristically expressive style, with energetic pencil strokes.
From this sketch, Van Gogh made his final drawing of Worn out, which belongs to the Van Gogh Museum. There are interesting differences between the sketch and final work. In the eventual drawing, the man sits more straightly on the chair and there are elements of a fireplace near his right leg. Vincent signed this work, confirming that it is the finished version.
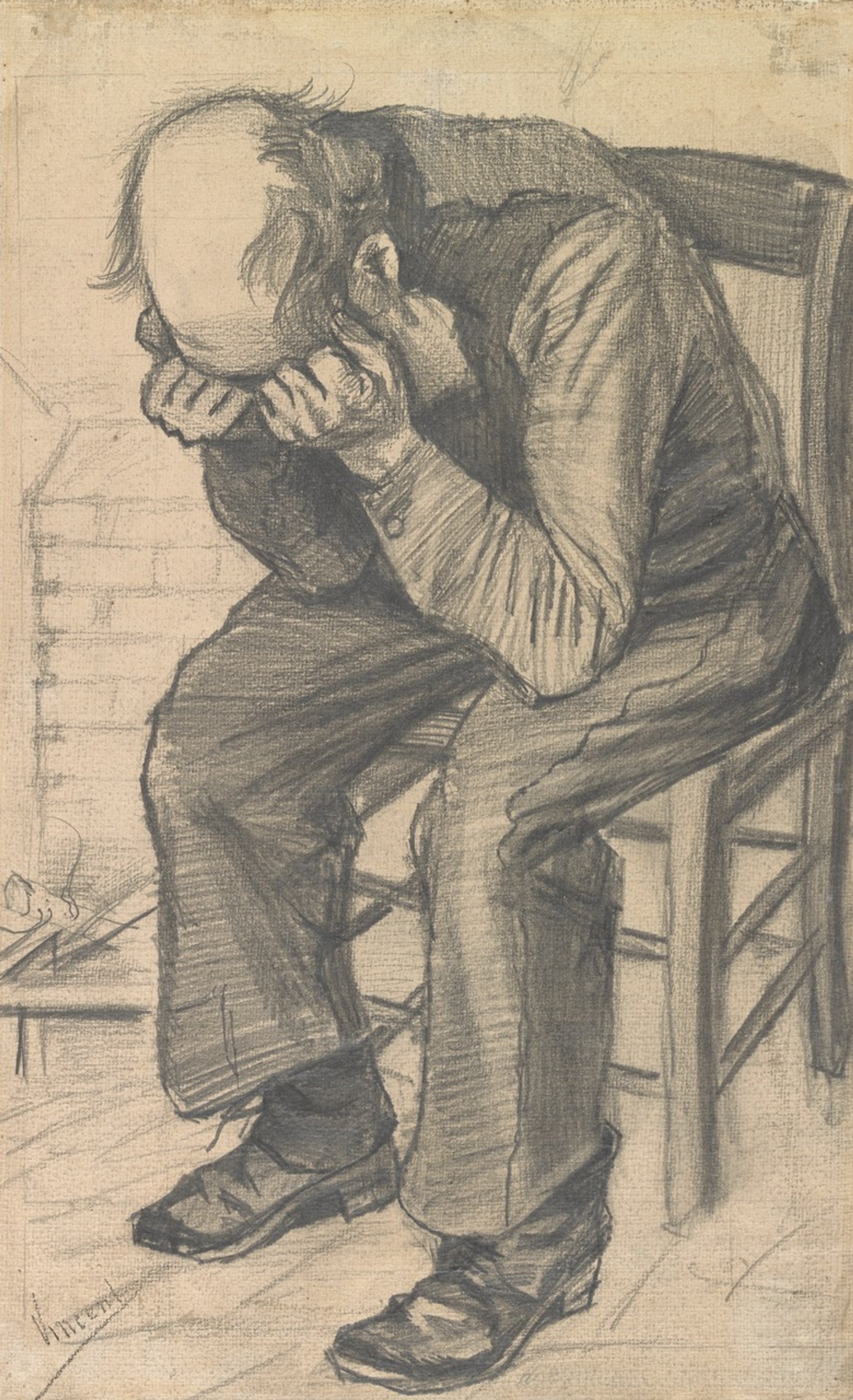

Van Gogh’s final version of Worn out (November 1882) Courtesy of the Van Gogh Museum, Amsterdam (Vincent van Gogh Foundation)
The model for Worn out was Adrianus Jacobus Zuyderland (1810-97), a 72-year-old resident of a local almshouse (Van Gogh called them “orphan men”). He appears in no fewer than 40 of Van Gogh’s drawings from The Hague, instantly recognisable from the bald crown of his head, longish white hair and impressive sideburns.
In making the composition, Van Gogh may have had in mind an illustration in a Dickens book. The frontispiece of an 1866 edition of Hard Times shows a very similar pose, drawn by Arthur Boyd Houghton. Van Gogh was a great admirer of Dickens, whose work he had got to know when he was a young art dealer in London.
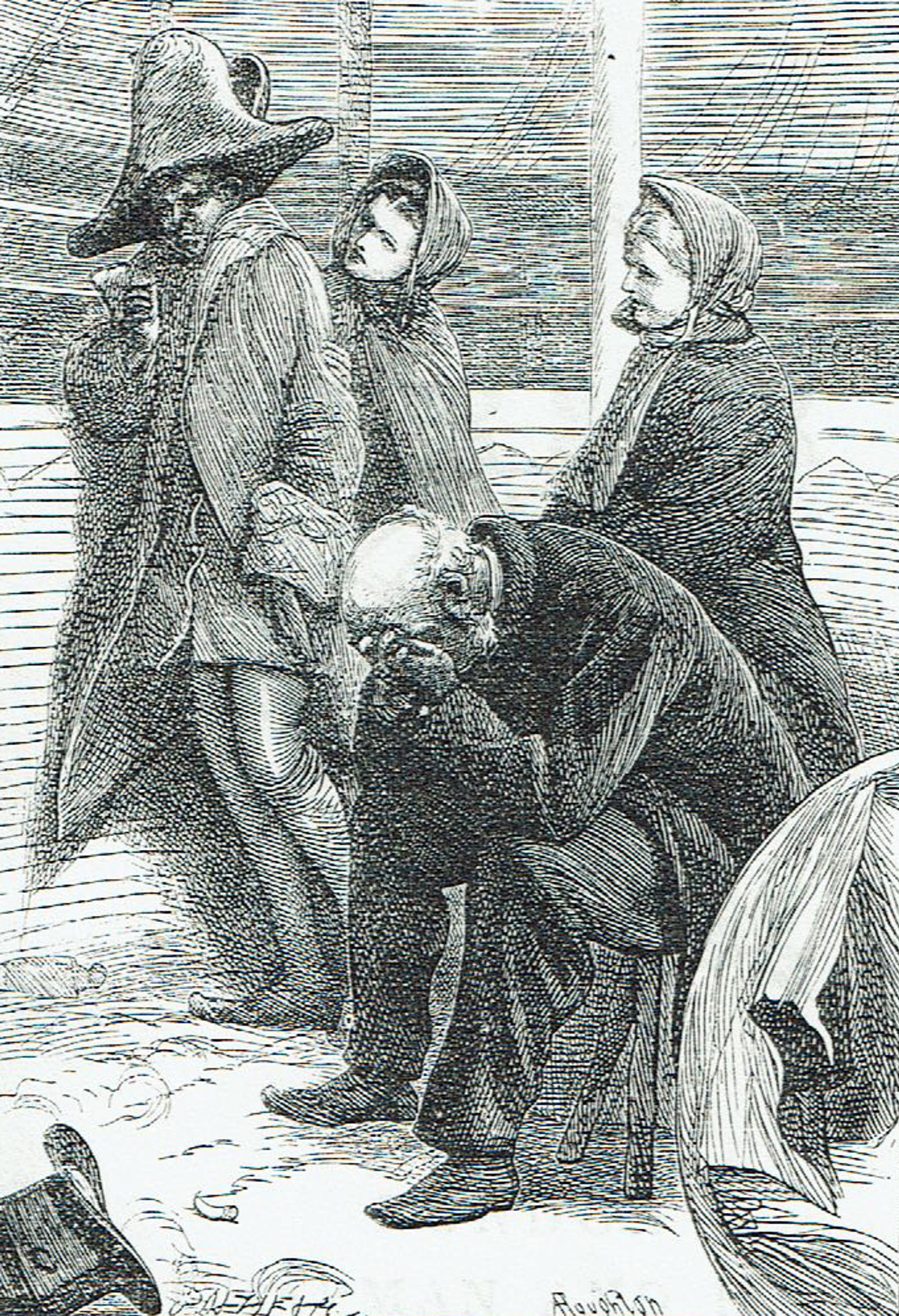

Arthur Boyd Houghton’s frontispiece for Dickens’ Hard Times (1866 edition), showing a seated Mr Gradgrind, after hearing that his son had robbed a bank
Vincent recorded doing both versions of Worn out in a letter to his brother Theo, on 24 November 1882: “Today and yesterday I drew two figures of an old man with his elbows on his knees and his head in his hands… What a fine sight an old working man makes, in his patched bombazine [a type of hard-wearing fabric] suit with his bald head.” The patch appears at the bottom of Zuyderland’s right trouser, but not on the finished drawing.
In another letter, to Vincent’s friend Anthon van Rappard, he entitled the drawing “Worn out”, in English. This was because Van Gogh then had the idea of seeking work as an illustrator with a British publication, either the Illustrated London News or the Graphic, and wanted some samples to send. It remains unclear whether he actually approached them—or if they rejected his work.
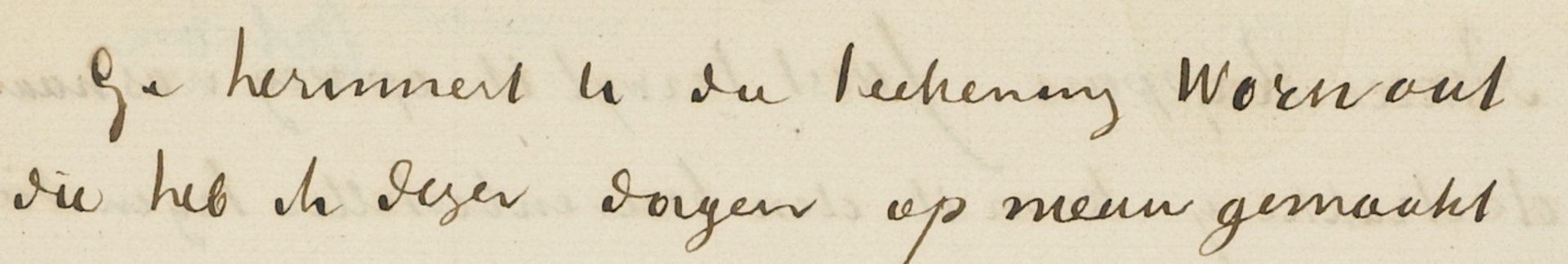
Extract of Vincent’s letter of 24 November 1882 in Dutch to Anthon van Rappard, giving the title “Worn out” in English Courtesy of the Van Gogh Museum, Amsterdam (Vincent van Gogh Foundation)
The expression “worn out” was widely used in English literature during the Victorian period, including in the writings of Dickens and Longfellow. Van Gogh may also have seen a print after a painting by the Scottish artist Thomas Faed with the same title (although the Faed composition is entirely different, showing a slumped father by the bedside of his seriously ill child).
Van Gogh was obviously proud of Worn out, since a few days later he made a lithograph based on the finished drawing. He gave this another English title, At Eternity’s Gate. Eight years later, at the asylum just outside Saint-Rémy-de-Provence, he used the print as the basis for his painting, with the figure clothed in shades of blue.
And how much is the newly discovered sketch worth? A family inventory suggests that in the early 1900s it was bought for 75 guilders, then equivalent to around £6. Drawings from Van Gogh’s period in The Hague now generally sell for up to €1m.
The sketch, along with the final drawing of Worn out and the lithograph, goes on display at the Van Gogh Museum tomorrow (until 2 January 2022).
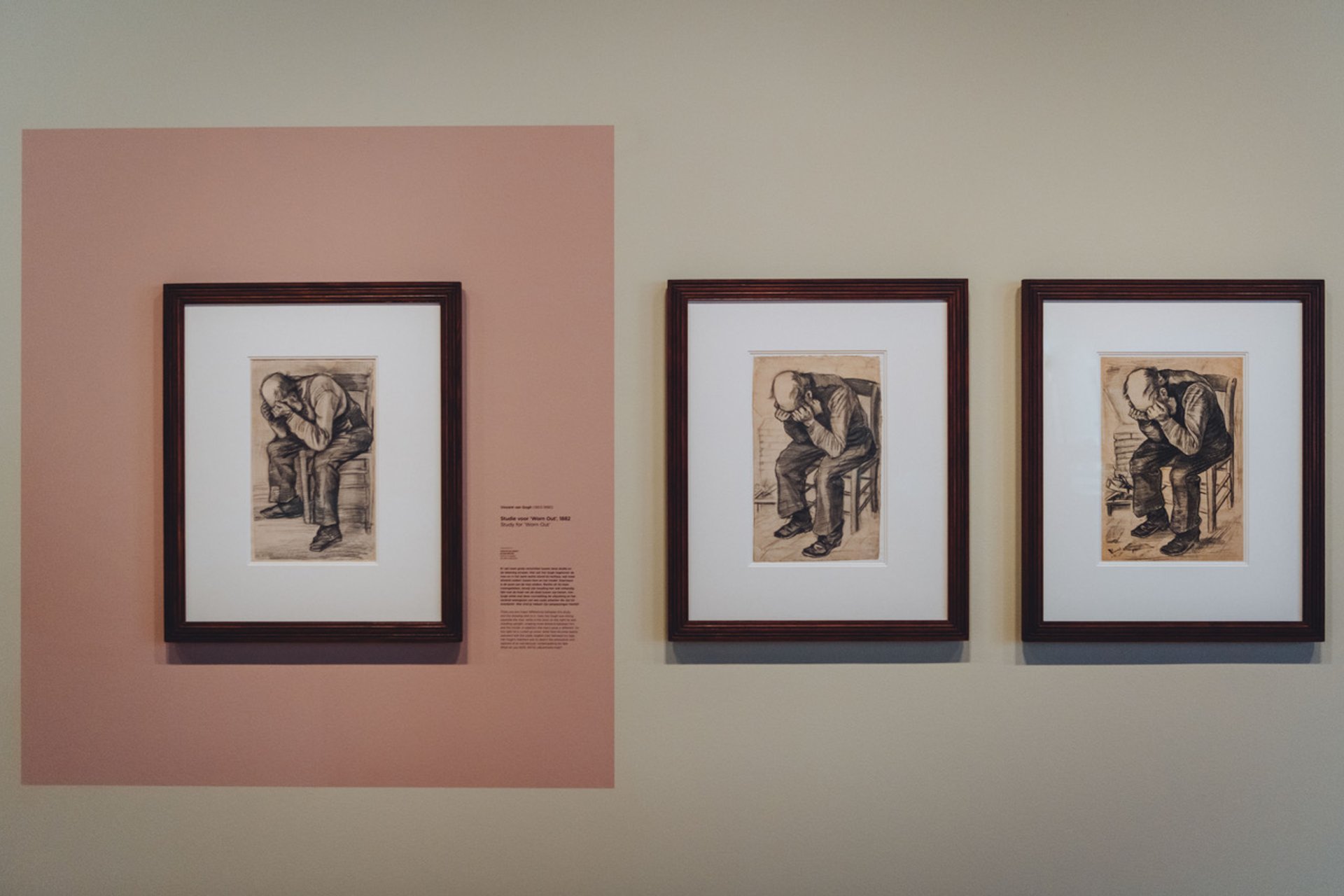

Display at the Van Gogh Museum—with the newly discovered sketch (on pink background), the drawing and the lithograph Courtesy of the Van Gogh Museum, Amsterdam; Photo: Jelle Draper
Other Van Gogh news
• A tiny fragment of an English text copied out in 1876 by Van Gogh in an album that once belonged to his landlady Annie Slade-Jones in Isleworth, west London, is on sale at a Connecticut auction house. The dismemberment of the album represents a tragic tale. In 1980 the entire album, with six pages of Van Gogh’s copied texts, sold at Sotheby’s for just £550. The Van Gogh pages were later extracted and dispersed, with the page from which this fragment comes being cut into at least seven fragments.

Van Gogh’s copied hymn “O Sacred Head, Now Wounded” (Van Gogh incorrectly wrote “Once” instead of “Now”), in an album belonging to Annie Slade-Jones (autumn 1876), to be auctioned by University Archives on 29 September
The University Archives company, based in Wilton, Connecticut, is offering one the pieces on 29 September, estimated at $40,000-$50,000. It comes from the collection of Noel Goldblatt, the owner of Chicago’s Goldblatt’s Department Store, who died in 2003; and then a Los Angeles collector. On one side of the fragment being sold Van Gogh copied 115 words in English from the hymn “O Sacred Head, Now Wounded” and on the reverse 36 words of a Dutch hymn. Below the English text someone has crudely added the inked words “VAN GOGH”.






