The National Gallery of Art (NGA), the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of African Art (NMAA) and the Rhode Island School of Design (RISD) Museum held a joint ceremony today (11 October) in Washington, DC, to mark the return of 31 Benin bronzes from their respective collections to Nigeria, marking the latest milestone in a growing movement to return the looted treasures.
The repatriation ceremony took place this morning behind closed doors at the NMAA, where 13 Benin objects have featured in a farewell display for the past two weeks. Nigeria’s National Commission for Museums and Monuments (NCMM) will now assume ownership of 29 artefacts that were deaccessioned earlier this year from the Smithsonian collections, including brass plaques, commemorative heads and figures.
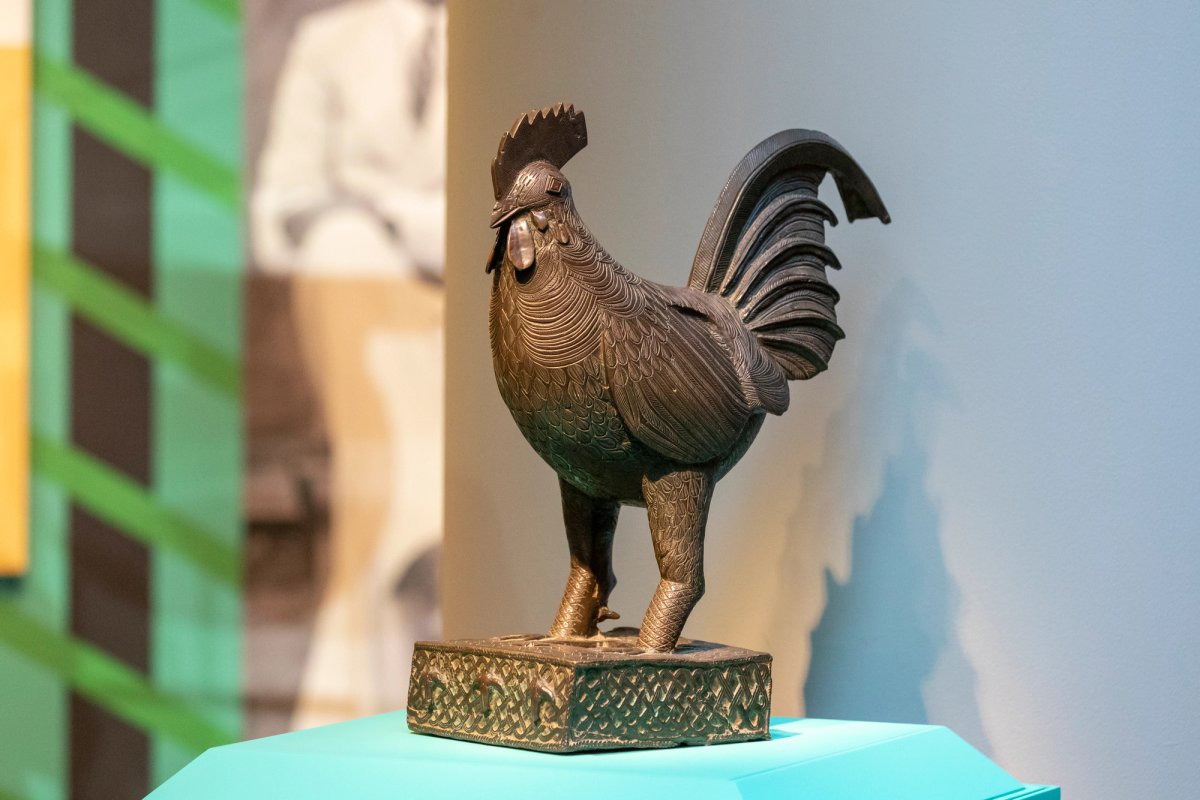
The NGA has repatriated a sculpture of a cockerel following a vote held in 2020 by its board of trustees to deaccession the work. The sculpture— the only Benin bronze in the museum’s collection—was first acquired by a British merchant who worked in Nigeria and consigned the piece to Sotheby’s London in 1954. It entered the museum’s collection in 1955 via donors who acquired the piece through the New York-based dealer John J. Klejman.
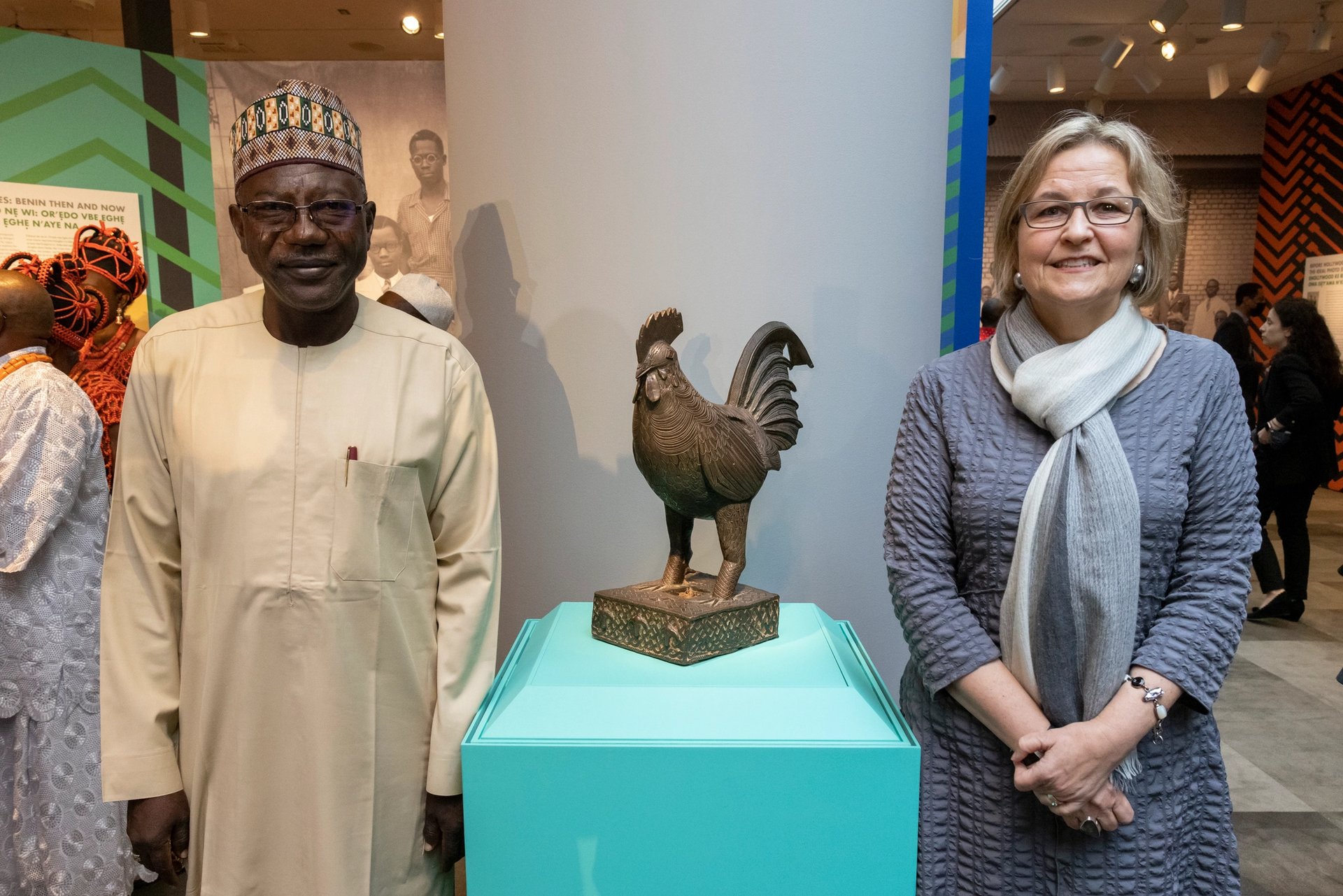

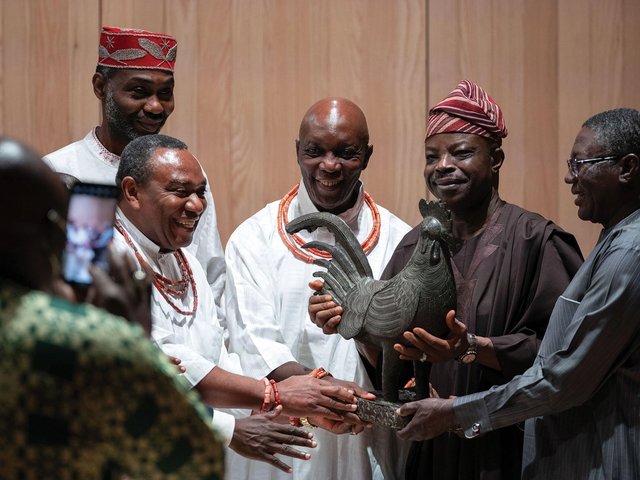
Professor Abba Isa Tijani, Director General of Nigeria's National Commission for Museums and Monuments and Kaywin Feldman, Director of the National Gallery of Art, with a Fowl sculpture previously in the collection of the National Gallery of Art. Courtesy National Gallery of Art.
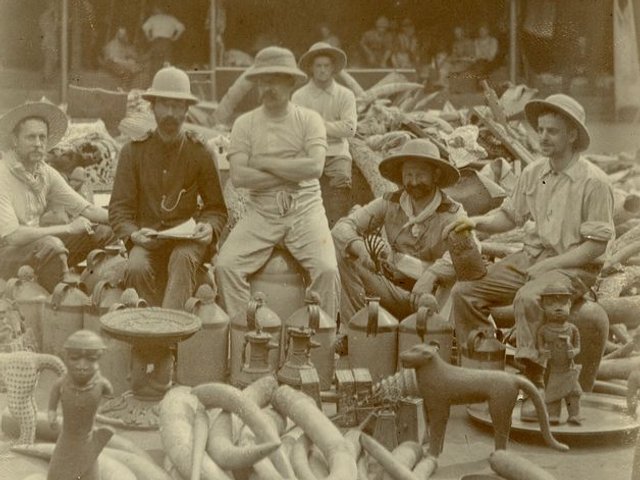
The cockerel was one of approximately 10,000 artefacts stolen by British troops from the royal palace in Benin in 1897. The pieces were dispersed throughout the world and, in the decades that followed, several were acquired by or donated to US museums including the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Chicago's Field Museum, the Museum of Fine Arts Boston and others
The repatriated pieces from NMAA and the NGA are joined by a bronze head of an Oba (king) from the RISD Museum, also deaccessioned in 2020. (The term “Benin bronzes” is a catch-all description encompassing objects in brass, ivory and wood as well as bronze.)
“This event opens a new vista regarding American cultural institutions’ relationship with Nigeria,” said Abba Isa Tijani, director general of the NCMM, hailing it as “a harbinger of greater things to come as other museums and institutions here in the United States with collections of Benin bronzes are expected to follow suit”.
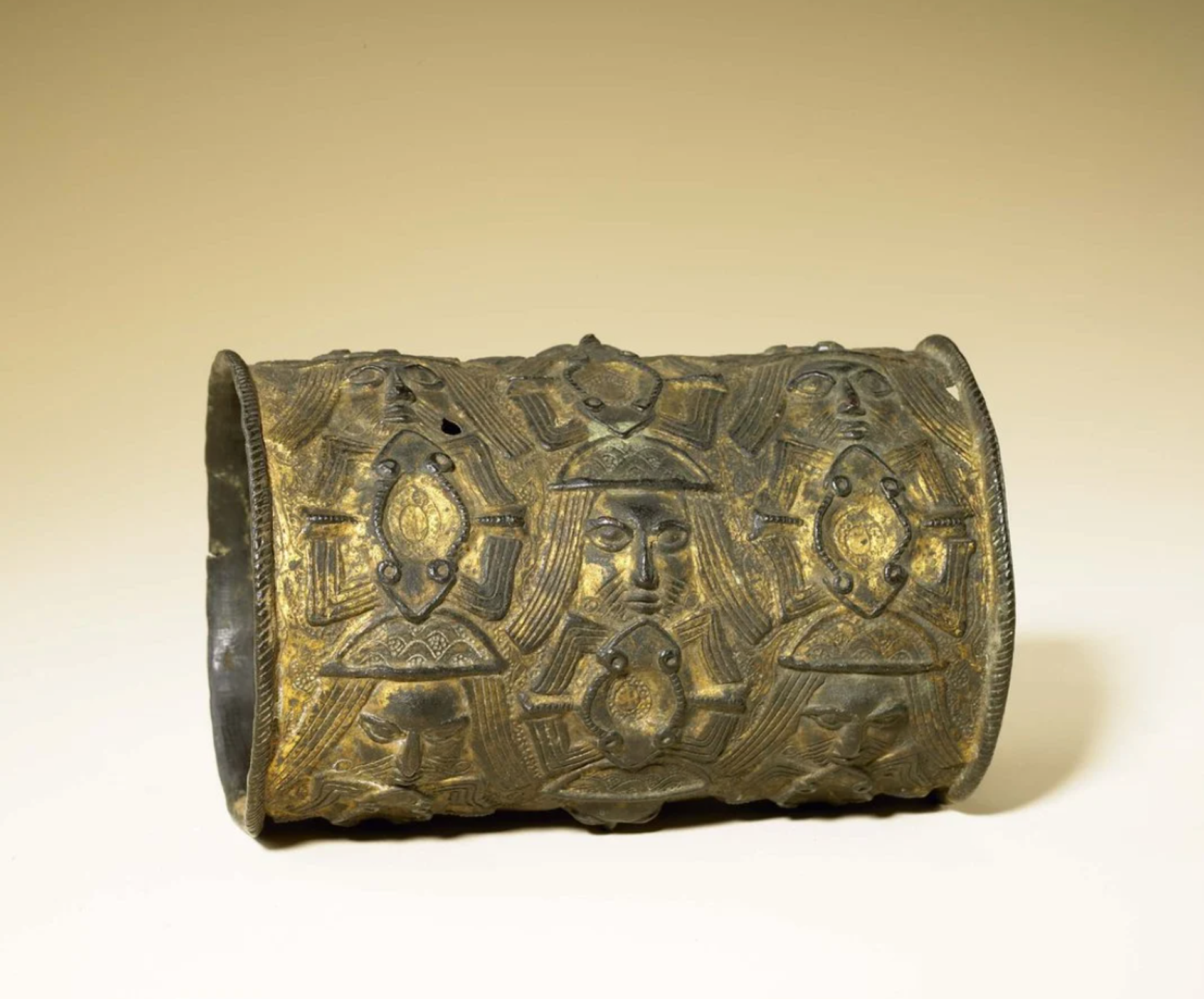

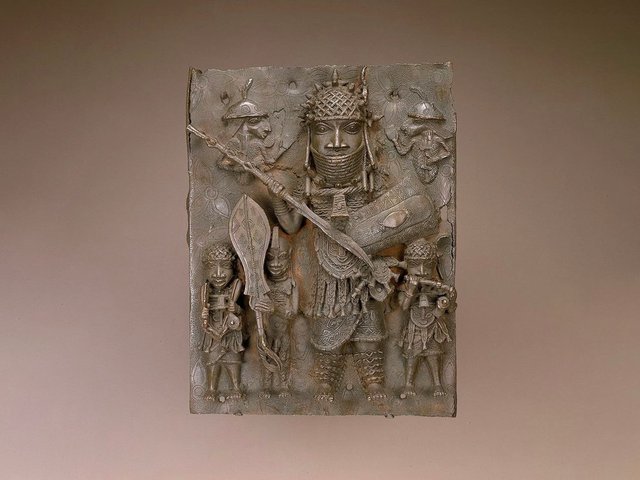
A bracelet by an Edo artist (17th-18th century) that was held by the NMAA. Smithsonian National Museum of African Art.
“By returning the artefacts, these institutions are together writing new pages in history,” said the Nigerian minister of information and culture Alhaji Lai Mohammed. He anticipated future collaborations between the NCMM and US museums, including joint exhibitions and educational exchanges. Under a new agreement, the NCMM will make nine Benin bronzes available to the NMAA as loans, a Smithsonian spokesperson says.
The Smithsonian announced the decision to return most of its Benin bronzes in March, several months after the objects were removed from display at the NMAA. “We cannot build for the future without making our best effort at healing the wounds of the past,” the museum’s director Ngaire Blankenburg told The Art Newspaper last November.
In June, the Smithsonian Board of Regents voted to deaccession 29 pieces that were definitively traced back to the 1897 British raid on Benin, in line with a new ethical returns policy adopted across the world’s largest museum complex. The policy authorises each of the Smithsonian’s 21 museums to deaccession and return objects that were acquired legally but in circumstances that are considered unethical today, including items that were stolen, taken under duress or removed without the consent of their owners. Twenty Benin items remain in the Smithsonian collections, pending further provenance research.
Today’s joint ceremony marks “another significant watershed in the global movement for restitution to African claimants”, says Dan Hicks, a professor of contemporary archaeology at the University of Oxford and the author of the 2020 book The Brutish Museums: the Benin Bronzes, Colonial Violence and Cultural Restitution. “The leadership offered by colleagues at the Smithsonian, National Gallery of Art and RISD is very welcome, and throws into relief the sustained silence and inaction in other significant collections, including the Metropolitan Museum and the British Museum.”
The Met repatriated two looted Benin items to Nigeria last November, but retains around 160 in its collection—one of the largest in the US. With more than 900 pieces, the British Museum in London has the world’s biggest collection of Benin bronzes.
“By their decision, the Smithsonian has allowed us to ask other museums that acquired looted Benin artefacts under the same circumstances whether they would continue to shield themselves with the dirty cloak of law, or with ethically sound institutional ideals,” says Chika Okeke-Agulu, a Nigerian artist, art historian and professor at Princeton University.
The return of the Benin bronzes to Nigeria “could contribute in significant ways to the necessary task of repair, of healing long-festering psychological wounds inflicted on Africans during that moment of violent, rapacious encounter with European colonial machinery and ideology”, he argues.
The Nigerian-American artist Victor Ehikhamenor, a trustee of the nonprofit that is building the future Edo Museum of West African Art in Benin City to house the Benin bronzes, describes the artefacts as “story books for us [Nigerians]” with immense cultural value for future generations. They are important both as spiritual symbols for rituals that can now be re-established in the palace of the latter-day Oba of Benin, he says, and as “visual cues that we can use to tell our children about the kind of life our ancestors led”.